As global temperatures continue to rise, the impacts of extreme heat on infrastructure, particularly railway systems, have become increasingly critical. Over the past several decades, railway authorities and surrounding communities have faced significant economic losses due to damaged infrastructure and resulting delays. Recently, a malfunctioning circuit breaker caused a power outage that shut down Amtrak’s trains along its Northeast Corridor amid a record-setting heat wave across the East Coast.
The year 2023 marked the warmest year on record globally, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) predicts that warmer-than-normal temperatures will continue to dominate much of the United States through this summer. Extreme heat can have numerous detrimental impacts on railway infrastructure, including short circuits and track buckling. Each of these issues can lead to cascading consequences, ranging from track failures to signal failures, ultimately causing train delays and other disruptions.
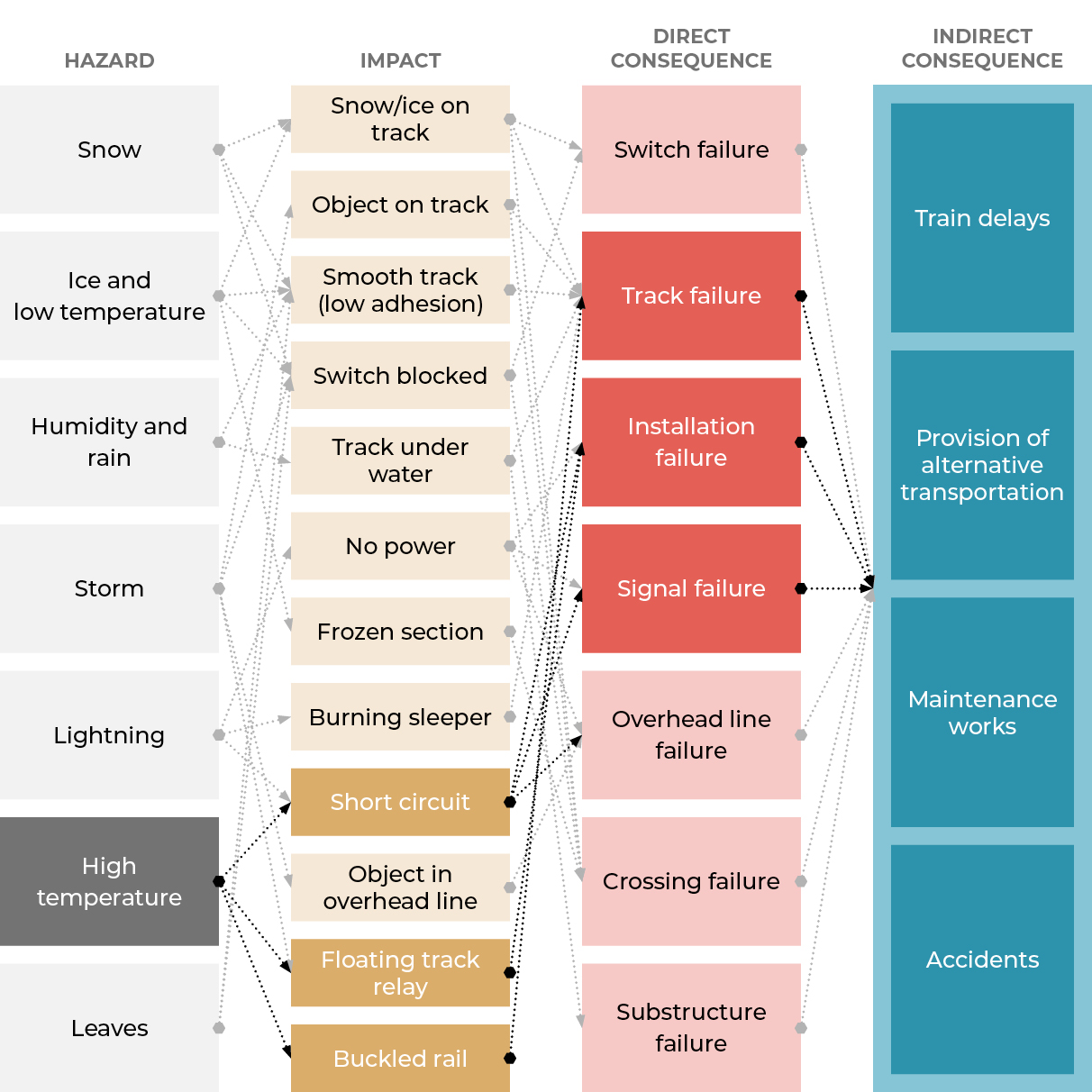
For STV, understanding future temperature trends and their impact on infrastructure vulnerability is vital for developing more resilient rail systems. In New Jersey, where STV has been supporting various rail and transit clients for decades, the state is experiencing a faster increase in average temperatures compared to the rest of the Northeast U.S., and the world. Additionally, by 2050, 70% of summers in the Northeast are expected to be hotter than the warmest summer to date.
To meet these challenges, our designers are anticipating temperature changes and incorporating climate projections into our planning and design approach to better safeguard rail systems. We leverage extensive industry expertise, coupled with ongoing research into emerging best practices, to develop design guidance and inform project decisions for climate adaptation. Our team recommends several design and operational best practices that can enhance the resilience of rail infrastructure against extreme heat:
Track System Installation
Continuous welded rail (CWR) is considered best practice for modern railroad installation due to its high performance and reduced maintenance needs. However, under high temperatures (rail temperatures can rise 40°F higher than ambient temperatures due to direct sunlight), thermal expansion and contraction can lead to increased longitudinal forces and potential lateral misalignment, making the rail susceptible to buckling—a known cause of train derailments. Mitigating this risk involves careful consideration of track design and material selection to enhance rail stability under extreme heat conditions.
Rail neutral temperature (RNT) is a crucial factor in mitigating buckling risk; it represents the temperature at which the rail is neither in tension nor compression. Determining the appropriate RNT involves considering local climate data and projected temperature trends. The Federal Railroad Administration (FRA) provides guidance on achieving the desired RNT through methods such as heating the rail, mechanically adjusting it or laying it once it has reached the neutral temperature due to ambient conditions. According to APTA’s Rail Transit Track Inspection Maintenance standards, variations in climate should be considered when determining RNT across a transit system. Accurate RNT ensures rail stability across diverse environmental conditions, reducing the likelihood of buckling during heatwaves.

Trackwork Elements
Beyond installation method, track elements can be leveraged to significantly increase lateral resistance and overall track stability. Proper lateral sizing of the ballast shoulder helps prevent rail buckling from thermal rail expansion. This critical design element outside of the ties for ballasted track sections contributes to lateral track stability. Additionally, choice of ties greatly impacts track performance. Frictional concrete ties offer higher lateral resistance than conventional concrete mono-block ties. Compared to timber alternatives, the higher weight of concrete ties can enhance lateral resistance and track integrity during extreme heat events.
Electrical Systems
Railway electrical systems are highly vulnerable to overheating. Historical incidents of transit electrical failures highlight the need for power source redundancy. As transit providers increasingly adopt low-carbon energy sources, incorporating redundant power options is essential for maintaining service continuity during extreme heat events. Leveraging diverse energy sources and implementing robust backup systems can prevent service disruptions and enhance the overall resilience of railway electrical infrastructure.
Overheating of signaling and communication systems, leading to service disruptions, is a common issue during extreme heat events. Automatic warning systems, traction power, track circuits and lineside equipment are particularly vulnerable. Strategies to mitigate overheating include ensuring proper ventilation, avoiding direct sunlight exposure and implementing low-cost monitoring systems at critical nodes; strategic landscaping and shade structures can also help reduce temperatures around electrical components. These measures are crucial for maintaining the functionality of railway systems during periods of extreme heat.
Site and Facility Considerations
Passenger and staff wellbeing is paramount during extreme heat. Adequate ventilation, air conditioning and passive cooling strategies, such as high-albedo materials and green roofs, are vital for maintaining comfort and safety at rail facilities. Additionally, increasing vegetation and implementing heat-resistant materials on site can further reduce heat absorption and improve thermal comfort.
Speed Limit Considerations
Emergency speed restrictions (ESRs) are standard operational practice during periods of extreme heat, aimed at preventing derailments due to rail buckling. These restrictions are based on temperature thresholds and vary across regions. For instance, Amtrak imposes speed limits of 100 mph when air temperatures exceed 98°F, and even stricter limits of 80 mph at temperatures above 102°F, along the Northeast Corridor. However, continuous advancements in climate modeling and sensing technologies offer opportunities for determining more precise temperature thresholds and operational protocols, providing potential pathways for mitigating operational delays.
Building climate-resilient rail infrastructure requires a multifaceted approach, integrating accurate climate projections, robust design practices and adaptive operational policies. While this article focuses on extreme heat, a comprehensive strategy must consider multiple climate hazards to ensure holistic infrastructure resilience. As climate change continues to pose complex risks, it is essential to incorporate these considerations into existing risk assessment and management frameworks. At STV, we are committed to leveraging our expertise to help clients navigate these challenges and build a resilient future for rail infrastructure.










